一、JDBC介绍
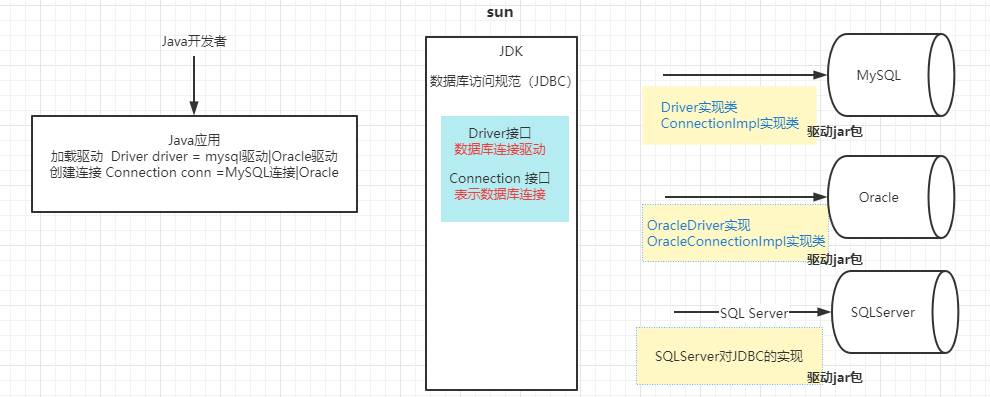
JDBC (Java DataBase Contectivity) Java与数据库的连接——数据库编程
JDBC 是Java语言(JDK)为完成数据库的访问操作提供的一套统一的标准。
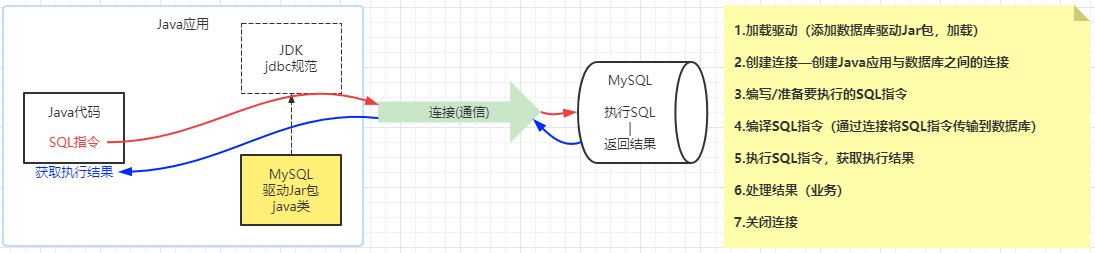
二、JDBC步骤
三、JDBC入门案例
JDBC 是用Java代码完成数据访问的规范
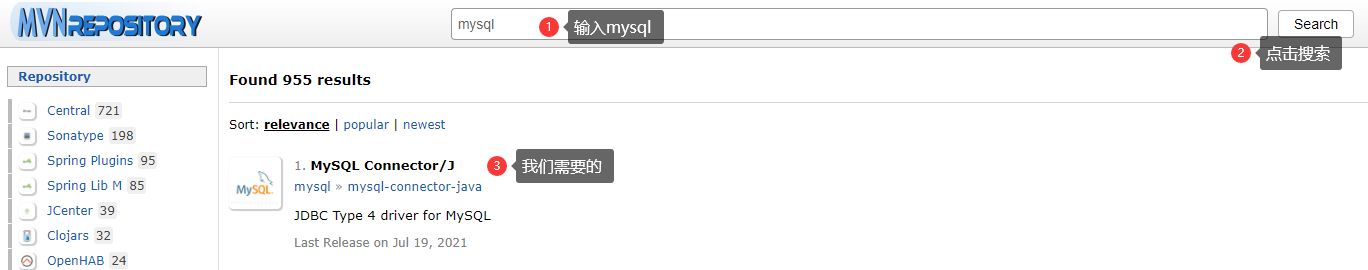
3.1 加载驱动 3.1.1 下载驱动jar包
对应数据库匹配版本的驱动jar包
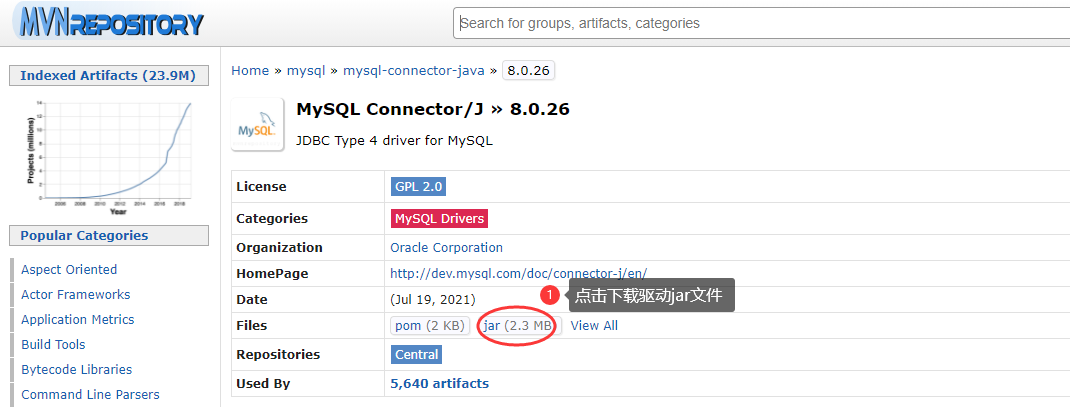
3.1.2 将驱动jar文件添加到Java应用
在java应用中创建lib文件夹
将下载好的jar文件拷贝—粘贴到lib目录
将驱动jar文件设置为java库:选择lib/驱动jar—右键—Add as Library.. —OK
3.1.3 注册驱动
通过反射机制,将驱动jar文件中提供的驱动类载入到JVM中
1 2 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" );
3.2 创建连接 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3" ;Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root" ,"@QFedu123" );
3.3 编写SQL指令 1 2 String sql = "insert into books(book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values('" +id+"','" +name+"','" +author+"'," +price+"," +stock+",'" +desc+"')" ;
3.4 加载SQL指令 1 2 3 4 Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
3.5 执行SQL、获取结果 1 2 3 4 5 6 int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
3.6 处理结果 1 2 3 4 5 6 System.out.println(i>0 ?"添加成功" :"添加失败" );
3.7 关闭连接 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 if (statement != null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection !=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); }
四、JDBC增删查改操作实例
使用JDBC完成数据库的CRUD访问
4.1 insert操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class TestInsertBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { String name = "Java进阶之路" ; String author = "老王" ; double price = 22.22 ; int stock = 10 ; String desc = "这本书很好" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root" ,"@QFedu123" ); String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values('" +name+"','" +author+"'," +price+"," +stock+",'" +desc+"')" ; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(i>0 ?"添加成功" :"添加失败" ); if (statement != null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection !=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
4.2 delete操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class TestDeleteBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { int bid = 1012 ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "delete from books where book_id=" +bid; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(i>0 ?"删除成功" :"删除失败" ); if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
4.3 update操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.sql.Statement;public class TestUpdateBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { int id = 1011 ; String name = "Java进阶之路" ; String author = "亮亮" ; double price = 36.80 ; int stock = 8 ; String desc = "这本书非常好" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "update books set book_name='" +name+"',book_author='" +author+"',book_price=" +price+",book_stock=" +stock +",book_desc='" +desc+"' where book_id=" +id; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println(i>0 ?"修改成功" :"修改失败" ); if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
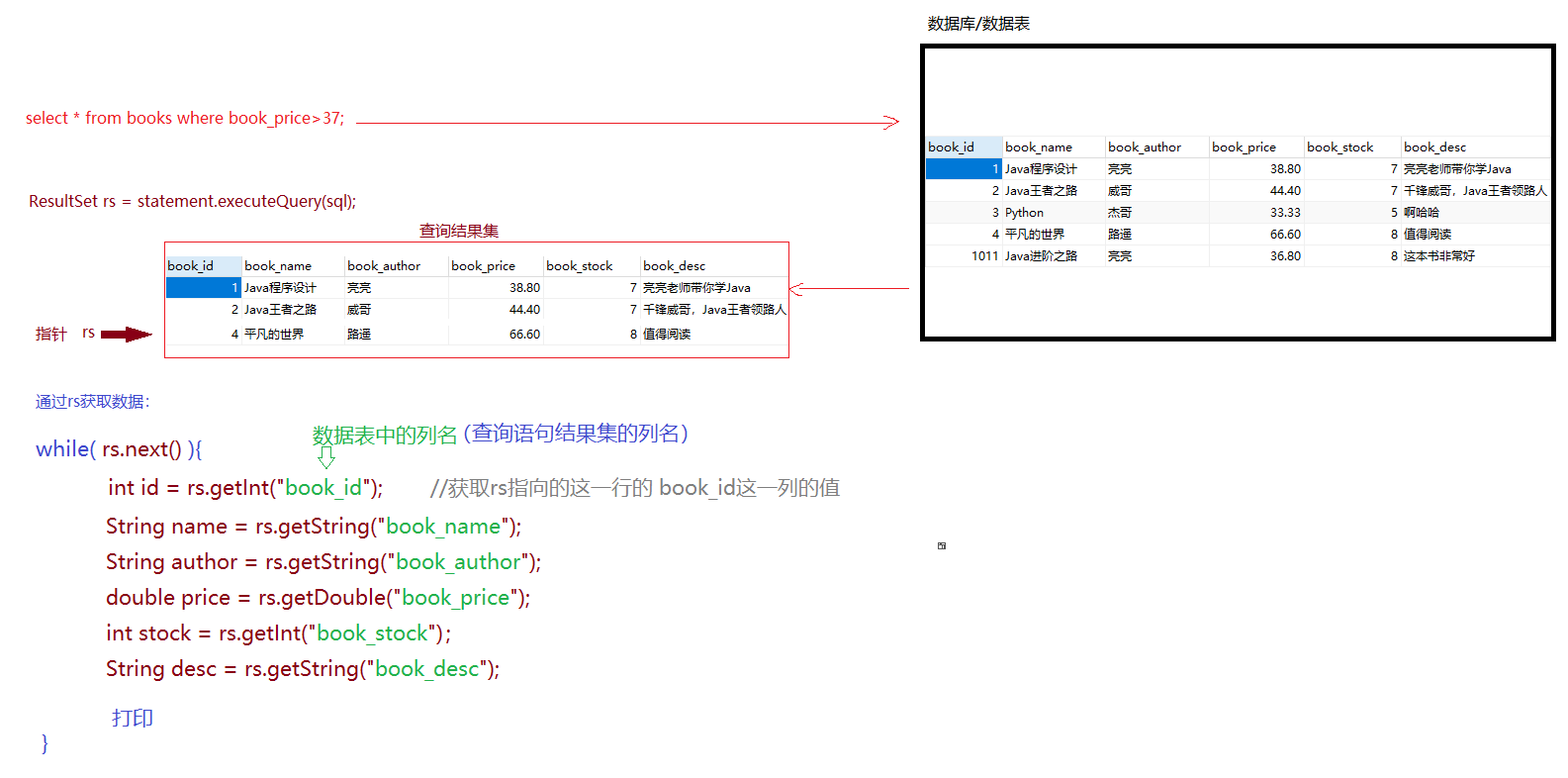
4.4 select操作(一条结果)
结果集处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import java.sql.*;public class TestSelectBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { int bid = 1011 ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=" +bid; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); if (rs.next()){ int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); System.out.println(bookId+"\t" +bookName+"\t" +bookAuthor+"\t" +bookPrice+"\t" +bookStock+"\t" +bookDesc); } if (rs!=null && !rs.isClosed()){ rs.close(); } if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
4.5 select操作(多条结果) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import java.sql.*;public class TestSelectBooks { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books" ; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()){ int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); System.out.println(bookId+"\t" +bookName+"\t" +bookAuthor+"\t" +bookPrice+"\t" +bookStock+"\t" +bookDesc); } if (rs!=null && !rs.isClosed()){ rs.close(); } if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
五、JDBC的核心类与接口
java.sql.DriverManager类 驱动管理器
java.sql.Connection接口 数据库连接
java.sql.Statement接口 SQL指令的“加载/执行器”
java.sql.ResultSet接口 结果集
5.1 DriverManager类
注册驱动
1 2 3 4 5 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" );
获取连接
1 2 3 4 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" );
5.2 Connection接口
Connection对象表示Java应用程序与数据库之间的连接
通过Connection接口对象,获取执行SQL语句的Statement对象
完成数据的事务管理
5.2.1 获取Statement对象
5.2.2 事务管理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 connection.setAutoCommit(false ); connection.rollback(); connection.commit();
5.3 Statement接口
用于编译、执行SQL指令的
1 2 3 4 5 int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
5.4 ResultSet接口
ResultSet接口对象,表示查询操作返回的结果集,提供了便利的方法用于获取结果集中的数据
判断结果集中是否还有数据未取出
1 2 3 4 ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(select_statement);rs.next();
获取rs指向的结果集中某行的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int id = rs.getInt(String columnLable); int id = rs.getInt(int columnIndex);rs.getString("" ); rs.getDouble("" ); .... rs.getDate("" );
六、SQL注入问题 6.1 什么是SQL注入问题?
在JDBC操作SQL指令编写过程中,如果SQL指令中需要数据,我们可以通过字符串拼接的形式将参数拼接到SQL指令中,如String sql = "delete from books where book_id="+s;(s就是拼接到SQL中的变量)
使用字符串拼接变量的形式来设置SQL语句中的数据,可能会导致因变量值的改变引起SQL指令的原意发生改变,这就被称为SQL注入。SQL注入问题是需要避免的。
例如:
如果s的值为1,SQL指令 : delete from books where book_id=1
如果s的值为1 or 1=1,SQL指令:delete from books where book_id=1 or 1=1
6.2 如何解决SQL注入问题?
使用PreparedStatement进行SQL预编译解决SQL注入问题:
在编写SQL指令时,如果SQL指令中需要参数,一律使用?参数占位符
如果SQL指令中有?,在JDBC操作步骤中不再使用Statement,而是从Conection对象获取PreparedStatement对SQL指令进行预编译 PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
预编译完成之后,通过PreparedStatement对象给预编译后的SQL指令的?复制
prepareadStatement.setInt(参数占位符序号,值);
prepareadStatement.setString(参数占位符序号,值);
SQL指令中的所有?完成赋值之后,通过PreparedStatement执行SQL执行SQL时不再加载SQL
int i = prepareadStatement.executeUpdate();
ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
6.3 使用PreparedStatement预编译案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver;import java.sql.*;import java.util.Scanner;public class TestDeleteBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要删除的图书的ID:" ); String s = scanner.nextLine(); int bid = Integer.parseInt(s); Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "delete from books where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(i>0 ?"删除成功" :"删除失败" ); if (preparedStatement!=null && !preparedStatement.isClosed()){ preparedStatement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import java.sql.*;public class TestInsertBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { String name = "Java进阶之路" ; String author = "老王" ; double price = 22.22 ; int stock = 10 ; String desc = "这本书很好" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root" ,"@QFedu123" ); String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,name); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,author); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,price); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,stock); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,desc); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(i>0 ?"添加成功" :"添加失败" ); if (preparedStatement != null && !preparedStatement.isClosed()){ preparedStatement.close(); } if (connection !=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import java.sql.*;public class TestUpdateBook { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { int id = 1011 ; String name = "Java进阶之路" ; String author = "亮亮" ; double price = 36.80 ; int stock = 8 ; String desc = "这本书非常好" ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root" , "@QFedu123" ); String sql = "update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,name); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,author); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,price); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,stock); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,desc); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(i>0 ?"修改成功" :"修改失败" ); if (preparedStatement!=null && !preparedStatement.isClosed()){ preparedStatement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1; import java.sql.* ; public class TestSelectBook { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { / / 根据图书ID,查询一本图书信息 int bid = 1013 ; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8"; Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "@QFedu123"); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql ); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); / / 通过executeQuery方法执行查询语句,并且将查询的结果存放到一个ResultSet对象中(结果集) ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); / / 处理结果:从rs中获取查询结果 if(rs.next()){ int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id"); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name"); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author"); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price"); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock"); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc"); System.out.println(bookId+ "\t"+ bookName+ "\t"+ bookAuthor+ "\t"+ bookPrice+ "\t"+ bookStock+ "\t"+ bookDesc); } / / 关闭连接 结果集也需要关闭 if(rs!= null && ! rs.isClosed()){ rs.close(); } if(preparedStatement!= null && ! preparedStatement.isClosed()){ preparedStatement.close(); } if(connection!= null && ! connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } } }
备注
七、工具类封装 7.1 代码的复用性 在我们的应用程序中,如果需要完成相同的操作,相同的代码无需重复编写,我们只需一次编写多次调用即可!
JDBC数据库编程是由一个固定的步骤:
注册驱动
创建连接
编写SQL
获取Statement对象
执行SQL
处理结果
关闭连接
7.2 工具类封装
DBManager
DBUtil
JDBCUtil
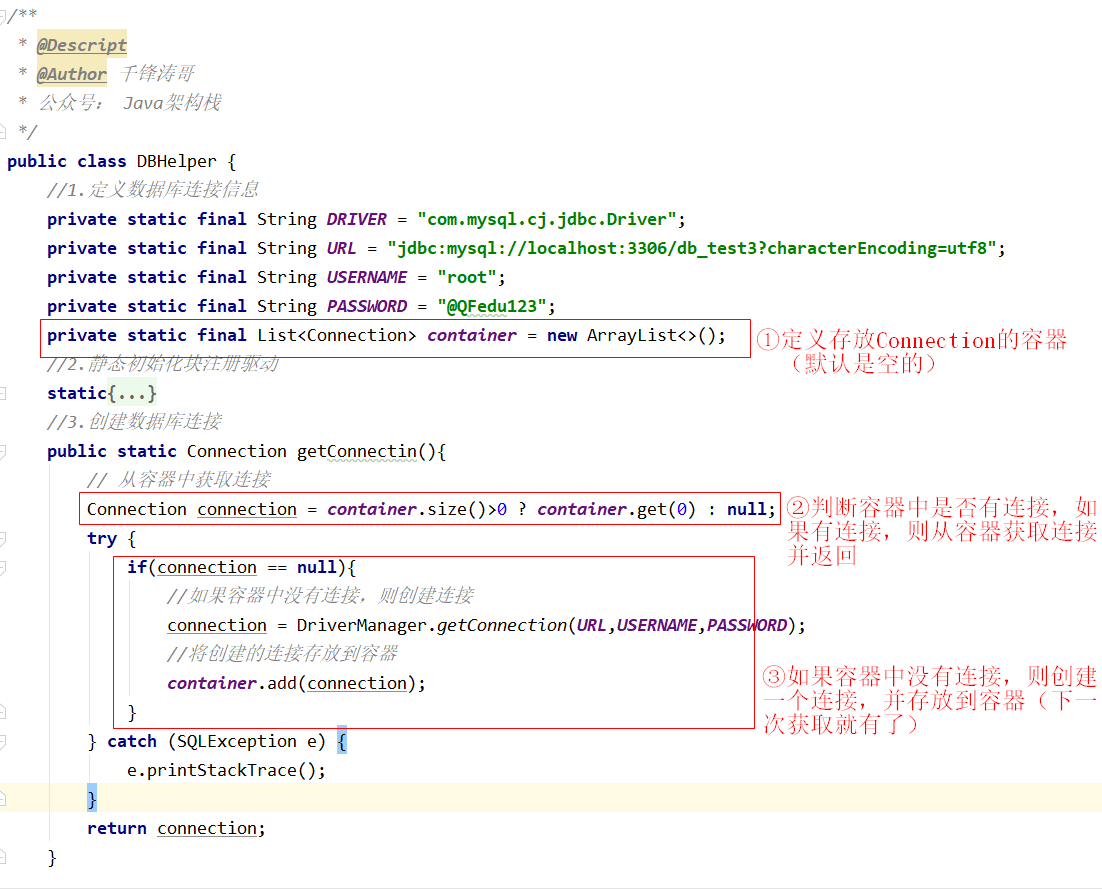
DBHelper
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import java.sql.*;public class DBHelper { private static final String DRIVER = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ; private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; private static final String USERNAME = "root" ; private static final String PASSWORD = "@QFedu123" ; static { try { Class.forName(DRIVER); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("-----------注册驱动失败" ); } } public static Connection getConnection () { Connection connection = null ; try { connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("-----------创建连接失败" ); } return connection; } public static void close (Statement statement, Connection connection) { close(null ,statement,connection); } public static void close (ResultSet resultSet,Statement statement, Connection connection) { try { if (resultSet!=null && !resultSet.isClosed()){ resultSet.close(); } if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("~~~~~关闭数据库连接失败" ); } } }
八、DAO与DTO的封装
DAO Data Access Object 数据访问对象
DTO Data Transfer Object 数据传输对象(实体类) 用于传输DML操作参数及DQL的查询结果
8.1 CRUD方法的封装
面向对象的特征之一——封装
我们将能够完成某个CRUD操作的代码单独定义成一个方法,当需要完成此CRUD操作时调用这个方法即可;
insert操作封装
delete操作封装
update操作封装
8.2 DTO实体类封装
问题:在封装CRUD方法时,对于查询操作而言,需要将查询到的数据库记录返回给调用者,但是一个查询方法只能返回一个值,而一条数据库记录有多个值,如何将一条数据库记录的多个值返回呢?
处理:在Java程序中创建一个属性与数据库表匹配的类,通过此类的对象封装查询到的数据,我们把用于传递JDBC增删查改操作的数据的对象称之为数据传输对象——DTO(实体类:带有属性,其对象可以存放数据的类)
实体类创建规则:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 * 1.类中属性的个数和类型,与对应的数据表保持一致 * 2.提供所有属性的get和set方法:Alt+Insert --- Getter And Setter --- 选择所有属性 --- OK * 3.提供全参构造器:Alt+Insert --- Constructor --- 选择所有属性 --- OK * 4.提供无参构造器:Alt+Insert --- Constructor --- SelectNone * 5.重写toString方法:Alt+Insert --- toString --- OK * 6.[暂略] 重写hashcode和equals * 7.[暂略]实现序列化Serializable接口
实体类实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dto;import java.io.Serializable;public class Book implements Serializable { private int bookId; private String bookName; private String bookAuthor; private double bookPrice; private int bookStock; private String bookDesc; @Override public String toString () { return "Book{" + "bookId=" + bookId + ", bookName='" + bookName + '\'' + ", bookAuthor='" + bookAuthor + '\'' + ", bookPrice=" + bookPrice + ", bookStock=" + bookStock + ", bookDesc='" + bookDesc + '\'' + '}' ; } public Book () { } public Book (int bookId, String bookName, String bookAuthor, double bookPrice, int bookStock, String bookDesc) { this .bookId = bookId; this .bookName = bookName; this .bookAuthor = bookAuthor; this .bookPrice = bookPrice; this .bookStock = bookStock; this .bookDesc = bookDesc; } }
使用实体类封装查询操作返回的结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public Book queryBook (int bid) throws SQLException{ Book book = null ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String name = rs.getString("book_name" ); String author = rs.getString("book_author" ); double price = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int stock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String desc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); book = new Book (id,name,author,price,stock,desc); } DBHelper.close(rs,preparedStatement,connection); return book; }
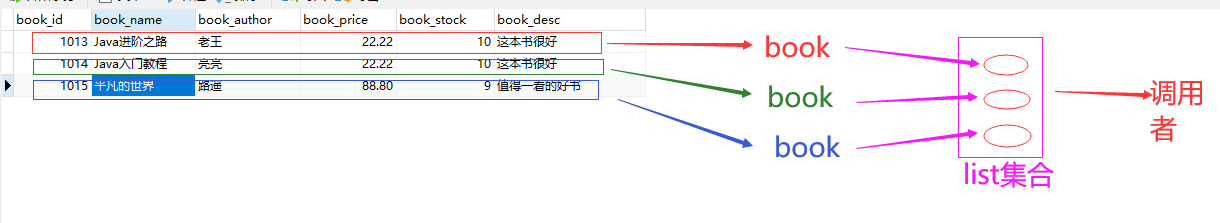
8.3 实体类封装查询结果
查询的每条结果分别存放到一个DTO对象中,再将多个DTO对象存放到一个List集合中,返回这个List集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.qfedu.jdbc.les1;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dto.Book;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class TestSelectBooks { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { List<Book> list = new TestSelectBooks ().listBooks(); for (Book b:list){ System.out.println(b.getBookName()+"\t" +b.getBookAuthor()); } } public List<Book> listBooks () throws SQLException{ List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList <>(); Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books" ; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()){ int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); Book book = new Book (bookId, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookStock, bookDesc); bookList.add(book); } DBHelper.close(rs,statement,connection); return bookList; } }
8.4 实体类传递添加、修改操作参数
在JDBC的添加、修改等方法中需要多个数据,我们可以通过实体类来进行参数传递
8.4.1 添加操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public boolean insertBook (Book book) throws SQLException { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,book.getBookDesc()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); return flag; }
8.4.2 修改操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean updateBook (Book book) throws SQLException{ boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,book.getBookDesc()); preparedStatement.setInt(6 ,book.getBookId()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); return flag; }
8.5 DAO类封装
DAO封装:将对数据库中同一张数据表的JDBC操作方法封装到同一个Java类中,这个类就是访问此数据表的数据访问对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class BookDAO { public boolean deleteBook (int bid) throws SQLException { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "delete from books where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); return true ; } public boolean insertBook (Book book) throws SQLException { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,book.getBookDesc()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); return flag; } public Book queryBook (int bid) throws SQLException{ Book book = null ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String name = rs.getString("book_name" ); String author = rs.getString("book_author" ); double price = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int stock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String desc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); book = new Book (id,name,author,price,stock,desc); } DBHelper.close(rs,preparedStatement,connection); return book; } public List<Book> listBooks () throws SQLException{ List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList <>(); Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books" ; Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()){ int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); Book book = new Book (bookId, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookStock, bookDesc); bookList.add(book); } DBHelper.close(rs,statement,connection); return bookList; } public boolean updateBook (Book book) throws SQLException{ boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,book.getBookDesc()); preparedStatement.setInt(6 ,book.getBookId()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); return flag; } }
8.6 DAO类代码优化
1.在应用程序开发中,如果方法中抛出异常且自己可以处理,则直接通过try/catch进行捕获处理;
2.JDBC操作方法的连接需要放在finally中进行关闭;
3.将数据库连接Connection、Statement、ResultSet等需要关闭的数据库对象定义在try之前;
4.因为所有的JDBC操作都需要Conection、Statement对象,查询方法都需要ResultSet对象,因此在DAO中可以将这些对象定义成类的成员变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dto.Book;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class BookDAO { private Connection connection; private Statement statement; private PreparedStatement preparedStatement; private ResultSet rs; public boolean deleteBook (int bid) { boolean flag = false ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "delete from books where book_id=?" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 ,bid); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); } return flag; } public boolean insertBook (Book book) { boolean flag = false ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 ,book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 ,book.getBookDesc()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); } return flag; } public Book queryBook (int bid) { Book book = null ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1 , bid); rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()) { int id = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String name = rs.getString("book_name" ); String author = rs.getString("book_author" ); double price = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int stock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String desc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); book = new Book (id, name, author, price, stock, desc); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { DBHelper.close(rs, preparedStatement, connection); } return book; } public List<Book> listBooks () { List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList <>(); try { connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books" ; statement = connection.createStatement(); rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { int bookId = rs.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = rs.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = rs.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = rs.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = rs.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = rs.getString("book_desc" ); Book book = new Book (bookId, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookStock, bookDesc); bookList.add(book); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(rs, statement, connection); } return bookList; } public boolean updateBook (Book book) { boolean flag = false ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnection(); String sql = "update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 , book.getBookName()); preparedStatement.setString(2 , book.getBookAuthor()); preparedStatement.setDouble(3 , book.getBookPrice()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 , book.getBookStock()); preparedStatement.setString(5 , book.getBookDesc()); preparedStatement.setInt(6 , book.getBookId()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i > 0 ; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement, connection); } return flag; } }
九、JDBC综合案例
完成学生信息的CRUD操作
9.1 JDBC数据库编程的流程
创建数据库、数据表
1 2 3 4 5 6 create table students( stu_num char (8 ) primary key , stu_name varchar (20 ) not null , stu_gender char (2 ) not null , stu_age int not null );
创建新的Java工程
创建JDBC的工具类:DBHelper
创建DTO类(用于封装参数及查询结果)
创建DAO类(用于完成CRUD操作)
9.2 创建JDBC工具类
在Java工程中创建package :com.qfedu.jdbc.utils
在com.qfedu.jdbc.utils包中创建工具类DBHelper
编写DBHelper工具类:
9.3 创建DTO类
9.4 创建DAO类
创建DAO类,完成JDBC操作
在Java项目中创建package:com.qfedu.jdbc.dao
在com.qfedu.jdbc.dao包中创建类StudentDAO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dto.Student;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class StudentDAO { private Connection connection; private Statement statement; private PreparedStatement preparedStatement; private ResultSet resultSet; public boolean insert (Student student) { boolean flag = false ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql = "insert into students(stu_num,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age) values(?,?,?,?)" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,student.getStuNum()); preparedStatement.setString(2 ,student.getStuName()); preparedStatement.setString(3 ,student.getStuGender()); preparedStatement.setInt(4 ,student.getStuAge()); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement,connection); } return flag; } public Student queryStudent (String snum) { Student student = null ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql = "select stu_num,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age from students where stu_num=?" ; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,snum); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (resultSet.next()){ String stuNum = resultSet.getString("stu_num" ); String stuName = resultSet.getString("stu_name" ); String stuGender = resultSet.getString("stu_gender" ); int stuAge = resultSet.getInt("stu_age" ); student = new Student (stuNum,stuName,stuGender,stuAge); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection); } return student; } public List<Student> listStudents () { List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList <>(); try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql = "select stu_num,stu_name,stu_gender,stu_age from students" ; statement = connection.createStatement(); resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (resultSet.next()){ String stuNum = resultSet.getString("stu_num" ); String stuName = resultSet.getString("stu_name" ); String stuGender = resultSet.getString("stu_gender" ); int stuAge = resultSet.getInt("stu_age" ); Student s = new Student (stuNum,stuName,stuGender,stuAge); studentList.add(s); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { DBHelper.close(resultSet,statement,connection); } return studentList; } }
9.5 测试DAO类中的方法
使用junit对DAO中创建的JDBC方法进行单元测试
9.5.1 下载导入junit依赖到项目中
下载:https://mvnrepository.com/ (如果使用junit 4.10 + 版本单元测试,需要以下两个jar文件)
junit-4.12.jar
hamcrest-core-1.3.jar
将junit-4.12.jar、hamcrest-core-1.3.jar拷贝项目的lib文件夹
选择拷贝到项目中的jar文件—右键—Add as Library
9.5.2 创建单元测试类
如果我们需要对某个类中的方法进行单元测试,我们需要创建这个类的测试类
StudentDAO ———> StudentDAOTest(测试类:类名=被测试类+Test)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package com.qfedu.jdbc.test;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dao.StudentDAO;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dto.Student;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.List;import static org.junit.Assert.*;public class StudentDAOTest { private StudentDAO studentDAO = new StudentDAO (); @Test public void testInsertStudent () { Student stu = new Student ("1008" ,"Tom" ,"男" ,20 ); boolean b = studentDAO.insertStudent(stu); assertTrue(b); } @Test public void testQueryStudent () { String snum = "1008" ; Student student = studentDAO.queryStudent(snum); assertEquals("Tom2" ,student.getStuName()); } @Test public void testListStudents () { List<Student> studentList = studentDAO.listStudents(); assertEquals(8 ,studentList.size()); } }
十、JDBC事务管理
什么是事务?
事务的四大特性—ACID
事务的隔离级别
MySQL事务管理:
start transaction
rollback
commit
10.1 JDBC实现借书操作
向records表添加借书记录
修改books表中的库存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;public class BookDAO { public boolean borrowBook2 (String stuNum,int bookId,int num) { boolean flag = false ; try { Connection connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql1 = "insert into records(snum,bid,borrow_num,is_return,borrow_date) values(?,?,?,0,sysdate())" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1); preparedStatement.setString(1 ,stuNum); preparedStatement.setInt(2 ,bookId); preparedStatement.setInt(3 ,num); int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); int k = 10 /0 ; Connection connection2 = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql2 = "update books set book_stock=book_stock-? where book_id=?" ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = connection2.prepareStatement(sql2); preparedStatement2.setInt(1 ,num); preparedStatement2.setInt(2 ,bookId); int j = preparedStatement2.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 && j>0 ; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { } return flag; } }
分析:
借书业务由两个数据库操作完成,这两个操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败,构成一个数据库事务;
JDBC的DML操作默认是自定提交的,因此当第一个DML操作(添加借书记录)完成后,无论第二个操作(修改库存)是否成功,借书记录都会添加到数据库,而且是永久的
JDBC中该如何做事务管理呢?
10.2 JDBC事务管理
一个事务中的多个DML操作需要基于同一个数据库连接;
创建连接之后,设置事务手动提交(关闭自动提交);connection.setAutoCommit(false);
当当前事务中的所有DML操作完成之后手动提交;connection.commit();
当事务中的任何一个步骤出现异常,在catch代码块中执行事务回滚。connection.rollback();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;public class BookDAO { public boolean borrowBook (String stuNum,int bookId,int num) { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = null ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = null ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = null ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); connection.setAutoCommit(false ); String sql1 = "insert into records(snum,bid,borrow_num,is_return,borrow_date) values(?,?,?,0,sysdate())" ; preparedStatement1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql1); preparedStatement1.setString(1 ,stuNum); preparedStatement1.setInt(2 ,bookId); preparedStatement1.setInt(3 ,num); int i = preparedStatement1.executeUpdate(); int k = 10 /0 ; String sql2 = "update books set book_stock=book_stock-? where book_id=?" ; preparedStatement2 = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); preparedStatement2.setInt(1 ,num); preparedStatement2.setInt(2 ,bookId); int j = preparedStatement2.executeUpdate(); connection.commit(); flag = i>0 && j>0 ; }catch (Exception e){ try { connection.rollback(); } catch (SQLException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement1,null ); DBHelper.close(preparedStatement2,connection); } return flag; } }
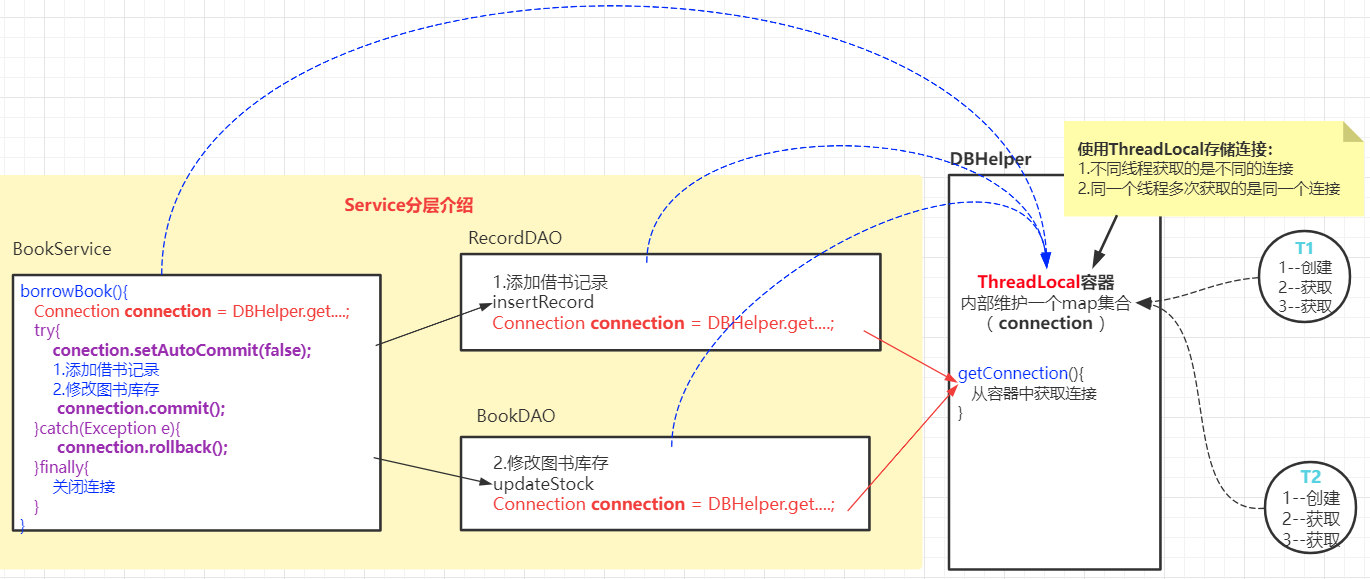
10.3 Service层的事务管理
DAO只负责数据库的操作,业务由service层进行管理
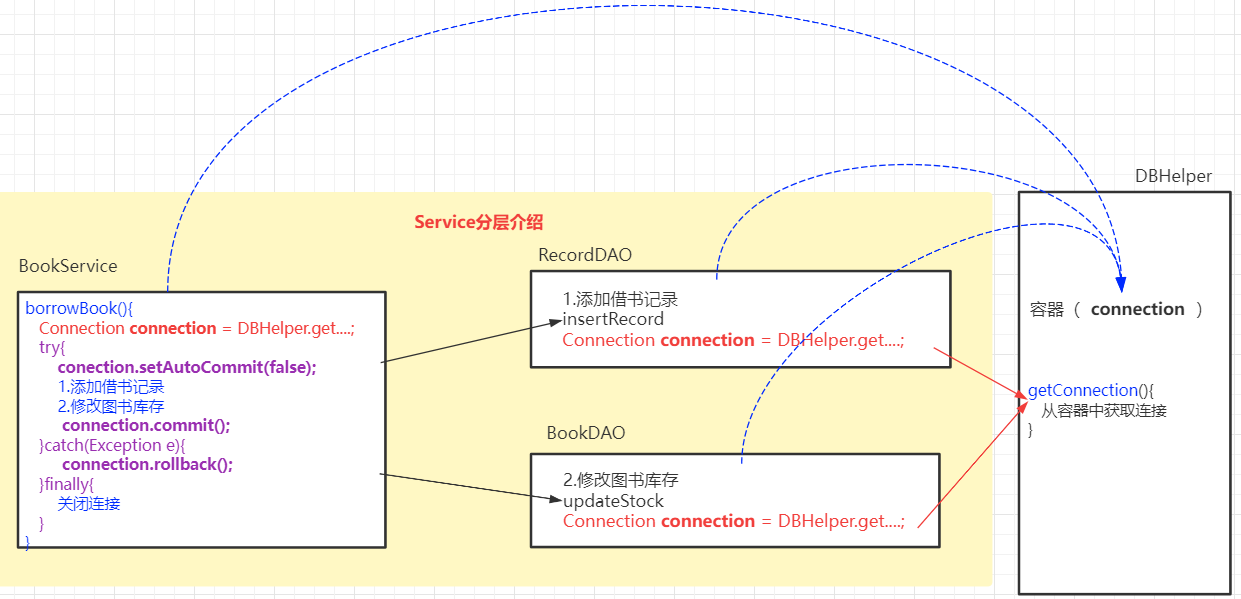
10.3.1 Service分层介绍
DAO负责特定的数据库操作
Servcie进行业务处理,Service业务处理过程如果需要数据库操作,则调用DAO完成
10.3.2 Service分层实现
创建RecordDAO,完成insertRecord方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;public class RecordDAO { public boolean insertRecord (String snum,int bid,int num) { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = null ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = null ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql1 = "insert into records(snum,bid,borrow_num,is_return,borrow_date) values(?,?,?,0,sysdate())" ; preparedStatement1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql1); preparedStatement1.setString(1 ,snum); preparedStatement1.setInt(2 ,bid); preparedStatement1.setInt(3 ,num); int i = preparedStatement1.executeUpdate(); flag = i>0 ; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement1,connection); } return flag; } }
在BookDAO中定义updateStock修改库存方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.DBHelper;import java.sql.*;public class BookDAO { public boolean updateStock (int bid,int num) { boolean flag = false ; Connection connection = null ; PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = null ; try { connection = DBHelper.getConnectin(); String sql2 = "update books set book_stock=book_stock-? where book_id=?" ; preparedStatement2 = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); preparedStatement2.setInt(1 ,num); preparedStatement2.setInt(2 ,bid); int j = preparedStatement2.executeUpdate(); flag = j>0 ; }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBHelper.close(preparedStatement2,connection); } return flag; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package com.qfedu.jdbc.service;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dao.BookDAO;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dao.RecordDAO;public class BookService { private RecordDAO recordDAO = new RecordDAO (); private BookDAO bookDAO = new BookDAO (); public boolean borrowBook (String stuNum,int bookId,int num) { boolean b1 = recordDAO.insertRecord(stuNum, bookId, num); boolean b2 = bookDAO.updateStock(bookId, num); boolean r = b1 && b2; return r; } }
10.3.3 Service层的事务管理
Servcie层事务中多个数据库的DML操作是相互独立的,如何保证所有DML要么同时成功,要么同时失败呢?
事务管理要满足以下条件:
多个DML操作需使用同一个数据库连接
第一个DML操作之前设置事务手动提交
所有DML操作执行完成之后提交事务
出现异常则进行事务回滚
如何让Service事务中的多个DML使用同一个数据库连接?
在Service获取连接对象,将连接对象传递到DAO中
分析:DAO类中的Connection对象需要通过Service传递给进来,这种对象传递本来也无可厚非,但是当我们通过面向接口开发时(面向接口,是为了能够灵活的定义实现类),容易造成接口的冗余(接口污染)
使用ThreadLocal容器,实现多个DML操作使用相同的连接
存储Connection的容器可以使用List集合
使用List集合做容器,在多线程并发编程中会出现资源竞争问题——多个并发的线程使用的是同一个数据库连接对象(我们的要求是同一个事务中使用同一个连接,而并非多个线程共享连接)
为了解决并发编程的连接对象共享问题,我们可以使用ThreadLocal作为数据库连接对象的容器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import java.sql.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class DBHelper { private static final String DRIVER = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ; private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8" ; private static final String USERNAME = "root" ; private static final String PASSWORD = "@QFedu123" ; private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> local = new ThreadLocal <>(); static { try { Class.forName(DRIVER); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConnectin () { Connection connection = local.get(); try { if (connection == null ){ connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USERNAME,PASSWORD); local.set(connection); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return connection; } public static void closeConnection () { Connection connection = local.get(); try { if (connection !=null && !connection.isClosed()){ connection.close(); } local.remove(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void closeStatement (Statement statement) { closeStatement(null ,statement); } public static void closeStatement (ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement) { try { if (resultSet!=null && !resultSet.isClosed()){ resultSet.close(); } if (statement!=null && !statement.isClosed()){ statement.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
十一、数据库连接池 11.1 什么是数据库连接池?
如果每个JDBC操作需要数据库连接都重新创建,使用完成之后都销毁,我们的JVM会因为频繁的创建、销毁连接而占用额外的系统资源。
数据库连接本质上是可被重用的资源(当一个JDBC操作完成之后,其创建的连接是可以被其他JDBC操作使用的),基于这个特性:
我们可以创建一个存放数据库连接的容器(连接池),连接池是有最大容量的
当我们要进行JDBC操作时,直接从这个容器中获取连接
如果容器中没有空闲的连接且连接池中连接的个数没有达到最大值,则创建新的数据库连接存入连接池并给这个操作使用,使用完成之后无需关闭连接直接归还这个容器中即可;
如果容器中没有空闲的连接且连接池中连接的个数达到最大值,当前操作就会进行等待,等待连接池中的某个连接被归还,归还之后再使用;
如果容器中有空闲连接,则无需创建新的连接,直接从容器中获取这个空闲连接进行使用;
连接池:存放数据库连接对象的容器
连接池作用:对数据库连接进行管理,减少因重复创建、销毁连接导致的系统开销
11.2 常用连接池
我们可以编程实现:创建一个数组、集合来存放数据库连接;
目前市面上已经有多种实现的数据库连接池了,我们无需再手动实现,只需引用对应的数据库连接池产品,即可在我们自己的Java应用中使用连接池(站在巨人的肩上)
功能
dbcp
druid
c3p0
HikariCP
是否支持PSCache
是
是
是
否
监控
jmx
jmx/log/http
jmx,log
jmx
扩展性
弱
好
弱
弱
sql拦截及解析
无
支持
无
无
代码
简单
中等
复杂
简单
特点
依赖于common-pool
阿里开源,功能全面
历史久远,代码逻辑复杂,且不易维护
优化力度大,功能简单,起源于boneCP
连接池管理
LinkedBlockingDeque
数组
ThreadLocal
基于连接池的性能、使用的便捷性、连接监控等多方面综合情况,druid是目前企业应用中使用最广泛的
Hikari在SpringBoot中默认集成,性能是诸多竞品中最好的
11.3 使用Druid连接池 11.3.1 创建Java应用
11.3.2 创建连接池属性配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # 数据库连接信息 driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8 username=root password=@QFedu123 # 连接池属性 # 连接池的初始化连接数<创建数据库连接池时默认初始化的连接的个数> initialSize=10 # 连接池的最大连接数 maxActive=50 # 最小空闲连接数(当数据库连接使用率很低时,连接池中的连接会被释放一部分) minIdle=5 # 超时等待时间(单位:ms) maxWait=30000
11.3.3 创建连接池工具类
十二、通用JDBC操作封装
在DAO层的JDBC操作中,对数据的表增、删、改、查操作存在代码的冗余,我们可以对其公共部分进行封装,实现代码的复用。
12.1 DML操作封装
对于数据库的DML操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;public class CommonDAO { public boolean update (String sql, Object... args) { boolean b = false ; try { Connection connection = DruidUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); b = i>0 ; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return b; } }
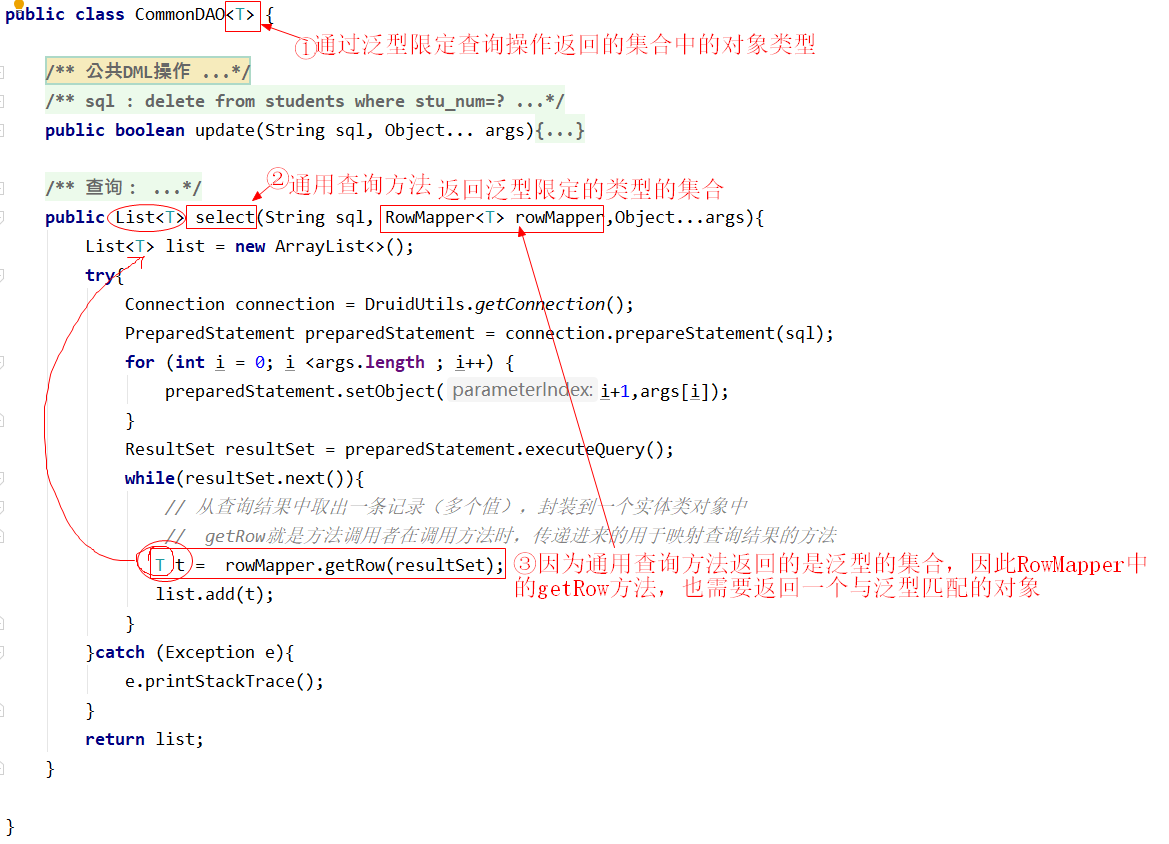
12.2 DQL操作封装
使用泛型设置通用查询方法的返回类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;public interface RowMapper <T> { public T getRow (ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class CommonDAO <T> { public boolean update (String sql, Object... args) { boolean b = false ; try { Connection connection = DruidUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); b = i>0 ; }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return b; } public List<T> select (String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper,Object...args) { List<T> list = new ArrayList <>(); try { Connection connection = DruidUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0 ; i <args.length ; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1 ,args[i]); } ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()){ T t = rowMapper.getRow(resultSet); list.add(t); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return list; } }
12.3 基于通用JDBC操作的案例
图书信息进行JDBC操作
12.3.1 创建实体类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Book { private int bookId; private String bookName; private String bookAuthor; private double bookPrice; private int bookStock; private String bookDesc; }
12.3.2 创建DAO类
DAO中的操作都是调用CommonDAO实现的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 package com.qfedu.jdbc.dao;import com.qfedu.jdbc.dto.Book;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.CommonDAO;import com.qfedu.jdbc.utils.RowMapper;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.List;public class BookDAO { private CommonDAO<Book> commonDAO = new CommonDAO <>(); public boolean insertBook (Book book) { String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; boolean b = commonDAO.update(sql, book.getBookName(), book.getBookAuthor(), book.getBookPrice(), book.getBookStock(), book.getBookDesc()); return b; } public boolean deleteBook (int bookId) { String sql = "delete from books where book_id=?" ; boolean b = commonDAO.update(sql, bookId); return b; } public boolean updateBook (Book book) { String sql="update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; boolean b = commonDAO.update(sql, book.getBookName(), book.getBookAuthor(), book.getBookPrice(), book.getBookStock(), book.getBookDesc(), book.getBookId()); return b; } public Book queryBook (int bookId) { String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?" ; RowMapper<Book> bookRowMapper = new RowMapper <Book>(){ public Book getRow (ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException { int bid = resultSet.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = resultSet.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = resultSet.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = resultSet.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = resultSet.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = resultSet.getString("book_desc" ); return new Book (bid,bookName,bookAuthor,bookPrice,bookStock,bookDesc); } }; List<Book> list = commonDAO.select(sql, bookRowMapper, bookId); return list.size()>0 ?list.get(0 ):null ; } public List<Book> listBooks () { String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books" ; List<Book> list = commonDAO.select(sql, resultSet -> { int bid = resultSet.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = resultSet.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = resultSet.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = resultSet.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = resultSet.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = resultSet.getString("book_desc" ); return new Book (bid, bookName, bookAuthor, bookPrice, bookStock, bookDesc); }); return list; } }
十三、Apache DBUtils 13.1 DBUtils介绍
Commons DBUtils是Apache组织提供的一个针对JDBC进行简单封装的开源工具类库,使用DBUtils可以极大简化JDBC应用程序开发,同时不会影响数据库访问的性能。
DBUtils是Java编程中数据库访问的轻巧、使用的工具类库
提供对数据表通用的DML操作
提供对数据表通用的DQL操作(可以把结果封装成对象、集合等类型)
DBUtils工具类库中的核心类:
13.2 DBUtils的使用准备
新建Java工程
添加依赖:
mysql-connector-java-8.0.26.jardruid-1.2.8.jarApache DBUtils建立数据库连接是依赖连接池数据源的,因此我们需要使用连接池commons-dbutils-1.7.jar
配置druid的属性文件
创建com.qfedu.jdbc.utils包
在包中创建druid.properties文件,配置如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 driverClassName =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_test3?characterEncoding=utf8 username =root password =@QFedu123 initialSize =10 maxActive =50 minIdle =5 maxWait =30000
创建Druid连接池工具类
在com.qfedu.jdbc.utils包创建DruidUtils工具类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package com.qfedu.jdbc.utils;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.Properties;public class DruidUtils { private static DruidDataSource druidDataSource; static { try { InputStream is = DruidUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("druid.properties" ); Properties properties = new Properties (); properties.load(is); druidDataSource = (DruidDataSource) DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static DataSource getDataSource () { return druidDataSource; } public static Connection getConnection () { Connection connection = null ; try { connection = druidDataSource.getConnection(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return connection; } }
13.3 DBUtils使用
完成图书信息的数据库操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Book { private int bookId; private String bookName; private String bookAuthor; private double bookPrice; private int bookStock; private String bookDesc; }
13.3.1 添加操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public int insertBook (Book book) { int i= 0 ; try { String sql = "insert into books(book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc) values(?,?,?,?,?)" ; Object[] params = {book.getBookName(),book.getBookAuthor(),book.getBookPrice(),book.getBookStock(),book.getBookDesc()}; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); i = queryRunner.update(sql, params); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return i; }
13.3.2 删除操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public int deleteBook (int bookId) { int i = 0 ; try { String sql = "delete from books where book_id=?" ; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); i = queryRunner.update(sql,bookId); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return i; }
13.3.3 修改操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int updateBook (Book book) { int i=0 ; try { String sql = "update books set book_name=?,book_author=?,book_price=?,book_stock=?,book_desc=? where book_id=?" ; Object[] params = {book.getBookName(),book.getBookAuthor(),book.getBookPrice(),book.getBookStock(),book.getBookDesc(),book.getBookId()}; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); i = queryRunner.update(sql, params); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return i; }
13.3.4 查询操作 查询一条记录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public Book queryBook (int bookId) { Book book = null ; try { String sql = "select book_id bookId,book_name bookName,book_author bookAuthor,book_price bookPrice,book_stock bookStock,book_desc bookDesc from books where book_id=?" ; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); book = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanHandler <Book>(Book.class), bookId); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return book; }
自定义结果集处理 自定义ResultSetHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public Book queryBook2 (int bookId) { Book book = null ; try { String sql = "select book_id,book_name,book_author,book_price,book_stock,book_desc from books where book_id=?" ; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); ResultSetHandler<Book> resultSetHandler = new ResultSetHandler <Book>() { @Override public Book handle (ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException { Book book = null ; if (resultSet.next()) { int id = resultSet.getInt("book_id" ); String bookName = resultSet.getString("book_name" ); String bookAuthor = resultSet.getString("book_author" ); double bookPrice = resultSet.getDouble("book_price" ); int bookStock = resultSet.getInt("book_stock" ); String bookDesc = resultSet.getString("book_desc" ); book = new Book (id,bookName,bookAuthor,bookPrice,bookStock,bookDesc); } return book; } }; book = queryRunner.query(sql, resultSetHandler, bookId); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return book; }
查询多条记录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public List<Book> listBooks () { List<Book> bookList = null ; try { String sql = "select book_id bookId,book_name bookName,book_author bookAuthor,book_price bookPrice,book_stock bookStock,book_desc bookDesc from books" ; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); bookList = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler <Book>(Book.class)); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return bookList; }
查询一个值
例如在做分页的时候,我们需要查询数据的总记录数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public long getCount () { long count = 0 ; String sql = "select count(1) from books" ; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner (DruidUtils.getDataSource()); ScalarHandler<Long> scalarHandler = new ScalarHandler <Long>(); try { count = queryRunner.query(sql, scalarHandler); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return count; }